Instruction Manual: 5G And Mobile Connectivity
Jargon Watch
Tech Jargon
C-V2X= Cellular vehicle-to-everything. C-V2X technology allows vehicles to “talk” to each other and to virtually any smart devices around them. This is a core technology envisioned to enable driverless cars.
SA and NSA= Standalone and non-standalone networks. Non-standalone 5G networks use existing 4G networks for connectivity and can only offer faster speeds, whereas 5G standalone networks can support and deliver full-fledged 5G capabilities, such as ultra-low latency.
Public Service Jargon
NBN= Nationwide Broadband Network. An ultra-high speed fibre broadband network that connects our homes and offices. This infrastructure enables Singapore’s digital economy and transformation into a Smart Nation.
DSL= Digital Services Laboratory. An engineering unit within the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) that partners research institutes and technology companies to tackle industry-level digitalisation challenges. Key engineering capabilities include AI, 5G and Internet of Things (IoT).
Say It Like This
i14y: Interoperability. A numeronym is a word where a number is used in an abbreviation because they sound alike (such as K9 for “canine”), or to signify the number of letters replaced in a long word. Interoperability is the ability of different computer systems to communicate and operate with other systems.
In Numbers
5G Benefits
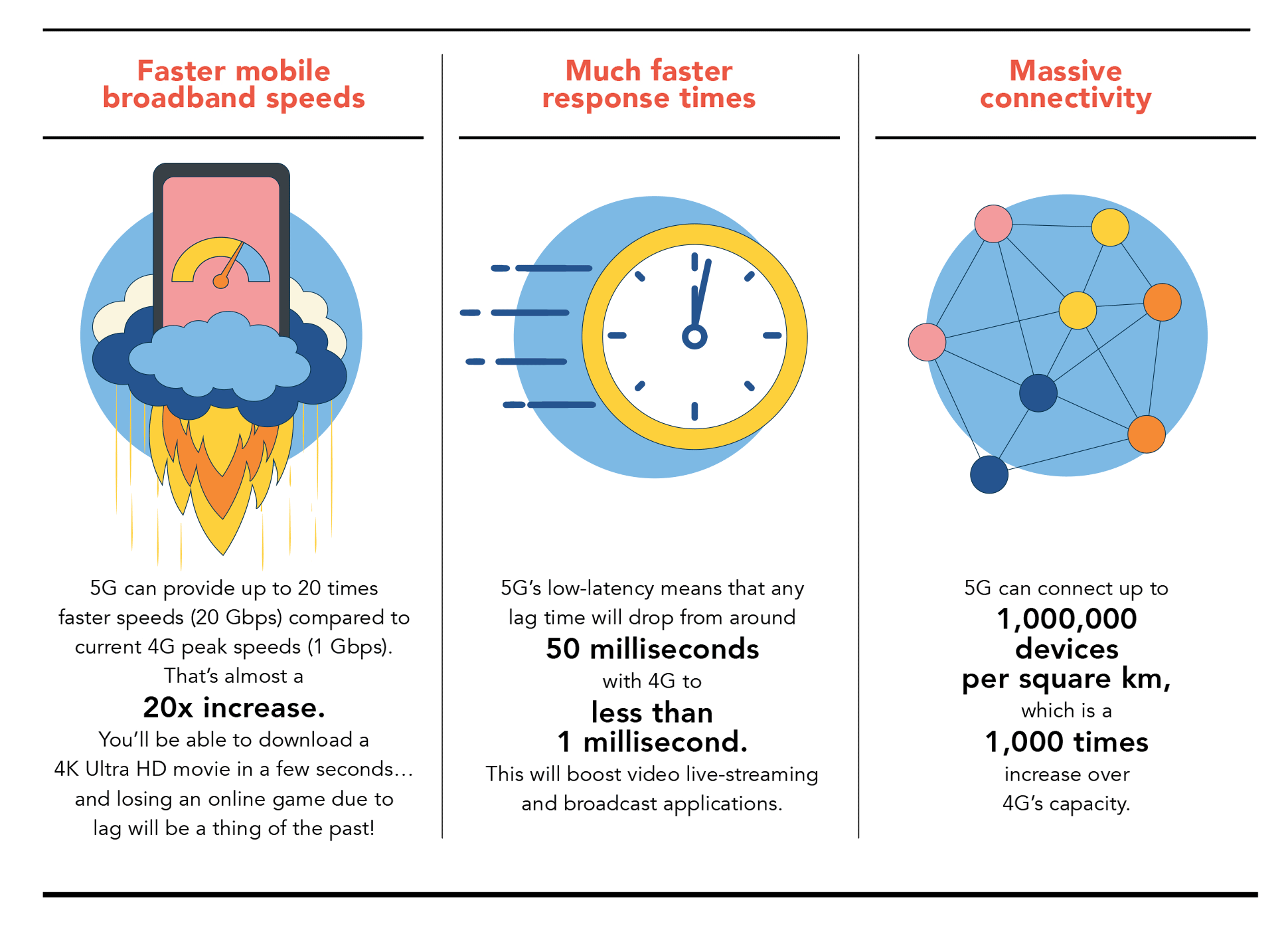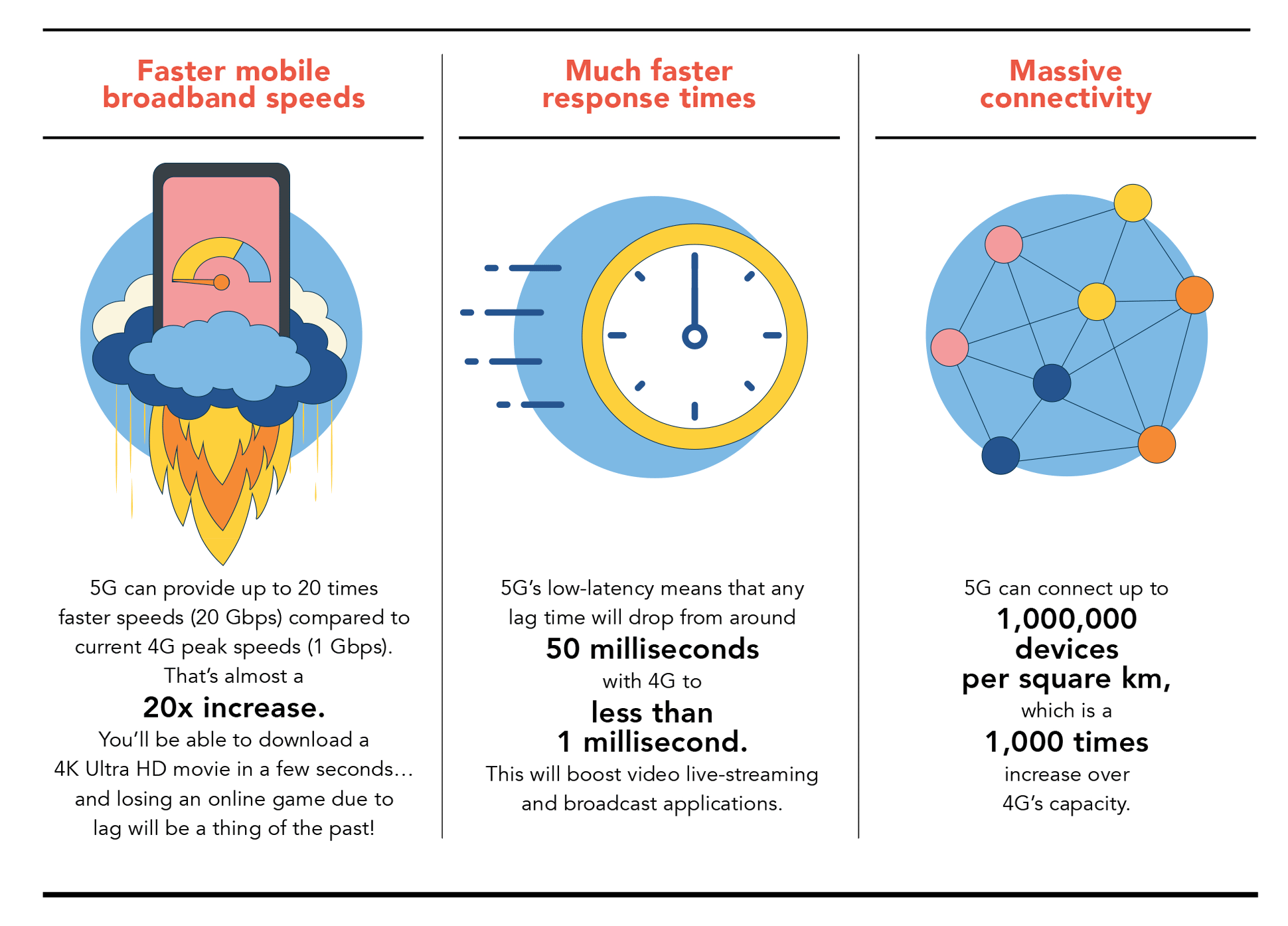
Faster mobile broadband speeds
5G can provide up to 20 times faster speeds (20 Gbps) compared to current 4G peak speeds (1 Gbps). That’s almost a 20x increase.
You’ll be able to download a 4K Ultra HD movie in a few seconds… and losing an online game due to lag will be a thing of the past!
Much faster response times
5G’s low-latency means that any lag time will drop from around 50 milliseconds with 4G to less than 1 millisecond. This will boost video live-streaming and real time applications.
Massive connectivity
5G can connect up to one million devices per square km, which is a 1000 times increase over 4G’s capacity.
Get Wired
Staying safe while using public Wi-Fi
With Wireless@SG and many places offering free Wi-Fi, learn how to stay safe and away from cybercriminals’ prying eyes while you surf.

Use HTTPS
Always check that the website you’re accessing uses HTTPS encryption. The ‘s’ stands for secure. Look for the https:// in front of the site URL or the padlock symbol in your browser’s address bar.
Avoid keying in sensitive info
Avoid using public Wi-Fi to key in private information such as login details (especially to bank accounts), your NRIC, home address, phone number or credit card details. Use a private Wi-Fi network or your mobile data instead.
Turn off wireless file-sharing
This prevents others from accessing your files or sending you unwanted files such as malware.
- For PC users, select “Turn off file and printer sharing” under Network settings.
- For Mac and iOS users, file-sharing options are under AirDrop settings.
Use a VPN
A virtual private network keeps your browsing private by encrypting the data travelling to and from your device. There are many free and paid VPN services available for different devices.
Related stories:
Want more? Join us on  Telegram to get alerts when new stories are published on Challenge.
Telegram to get alerts when new stories are published on Challenge.
- POSTED ON
Dec 12, 2019
- ILLUSTRATION BY
Mushroomhead
-
Work Better
Instruction Manual February 2018








