Metaverse: The Next Digital Frontier
A Trend to Watch
In 2021, the term “metaverse” gained worldwide attention as Facebook rebranded to “Meta”. The name reflects its ambition to build a metaverse, a social network elevated to that of 3-D virtual worlds.
But metaverse isn’t a new word – it was coined by Neal Stephenson in his 1992 dystopian sci-fi novel Snow Crash, which explored the concept of a virtual reality world.
Typically, the Internet is viewed through the screens of our devices. The idea of a metaverse takes this a step further to be an Internet with a tangible living experience.
Envisioned as the next evolution of the Internet, the metaverse lets users appear as customisable avatars, who can teleport from one virtual world to another. With the help of extended reality technologies, our living realities would be enmeshed with digital realities.
For a 360-viewing experience in the metaverse, virtual reality headsets or augmented reality glasses should be donned. However, these items pose a barrier to entry due to hefty price tags and the discomfort experienced after prolonged usage.
Nonetheless, smartphones and laptops can be used to access metaverse platforms like Decentraland and Roblox. Several public officers are already attending online courses about the metaverse.
As the appetite for the metaverse grows, big brands like Gucci and Balenciaga have already established their presence in it by offering their signature products in virtual form. It is predicted that 30% of organisations in the world will have products and services available for the metaverse by 2026.
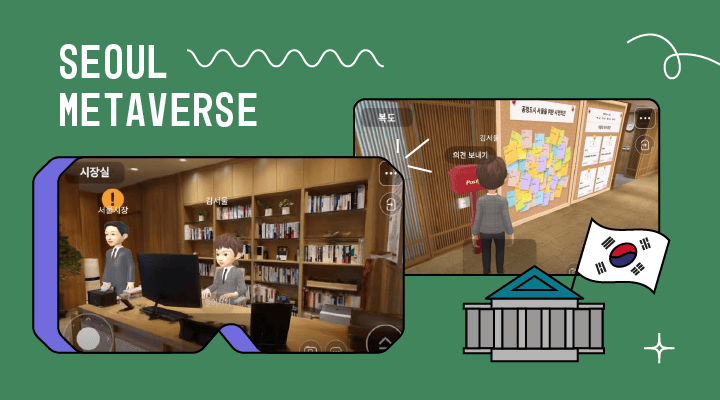
Global Outlook
Several nations are exploring the metaverse concept to make public services more convenient, boost tourism offerings and heighten public engagement.
South Korea
South Korea has invested 4.2 million dollars into a “Seoul Metaverse”. It aims to create a digital twin of the city with public services and cultural events that are accessible to all. By 2023, citizens will be able to walk up the steps of a virtual city hall and speak to public officials about their concerns within the comfort of their homes.
United Arab Emirates
The Ministry of Health and Prevention has launched the world’s first Metaverse Customer Happiness Centre. At the virtual centre, customers can make enquiries, request services, and settle administrative tasks without ever stepping into a physical space. The ministry plans to have an extensive rollout of services in the metaverse to enhance its citizens’ quality of life, especially for those with mobility issues.
China
Chinese tech companies like Baidu, Tencent and Byte Dance are heavily invested in the metaverse with aspirations to create new experiences and retain their users. For example, Baidu’s metaverse, Xi Rang, enables users to explore virtual environments and socialise. With the metaverse being multi-faceted, Baidu hopes to use it for gaming, entertainment and educational purposes.
Barbados
In a bid to push digital diplomacy, Barbados recently opened its first virtual embassy on metaverse platform Decentraland. This strategic move was cost-effective for the small island nation, as this virtual embassy costs a fraction of running a physical embassy. Visiting the virtual embassy is convenient and immersive, and there are plans to set up more embassies in the metaverse.

The US
Santa Monica, a shopping district in California, created a metaverse social app called “Santa Monica Metaverse”. Inspired by TikTok and Pokemon Go, the app encourages people to explore Santa Monica through an immersive metaverse experience. Users can unlock digital collectibles and use them to redeem goods from physical retailers. By showcasing digital art and photobooth locations on the app, the district hopes to generate interest and boost visitors.
Celebrate NDP in the Metaverse
Fulfil your National Day Parade aspirations in the metaverse by performing a free-fall as a Red Lion, zooming around in an armoured vehicle, and role-playing as military personnel with friends!
Learn the Lingo
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses all forms of immersive realities.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Technology that directly overlays digital objects onto the real world, such as the BalikSG app that makes local history come alive.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Technology that creates a fully immersive virtual environment via virtual reality headsets, such as for training lifesavers at the Civil Defence Academy.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Technology that makes digital objects responsive to changes in a real-world environment via mixed reality goggles, such as for surgical and educational purposes.
Digital twins: Responsive virtual replicas of places using real-time data tracking, employed in Virtual Singapore to aid urban planning.
A Tip on How To Recycle Right:
The Materials To Recycle

You can recycle metal, paper, glass, and plastic in the blue recycling bins, but sorting them is not necessary. The separation of materials is done at the Materials Recovery Facilities. If you’re unsure of what can or cannot be recycled in the blue bins, you may check using the Recycling Search Engine at www.cgs.gov.sg/recyclingsearch.
- POSTED ON
Jul 14, 2022
- TEXT BY
LEI NG
- PHOTOS BY
FLICKPLAY
SEOUL METROPOLITAN GOVERNMENT
- ILLUSTRATION BY
LEI NG









